Evolution of Artificial Neurons
Human Neurons
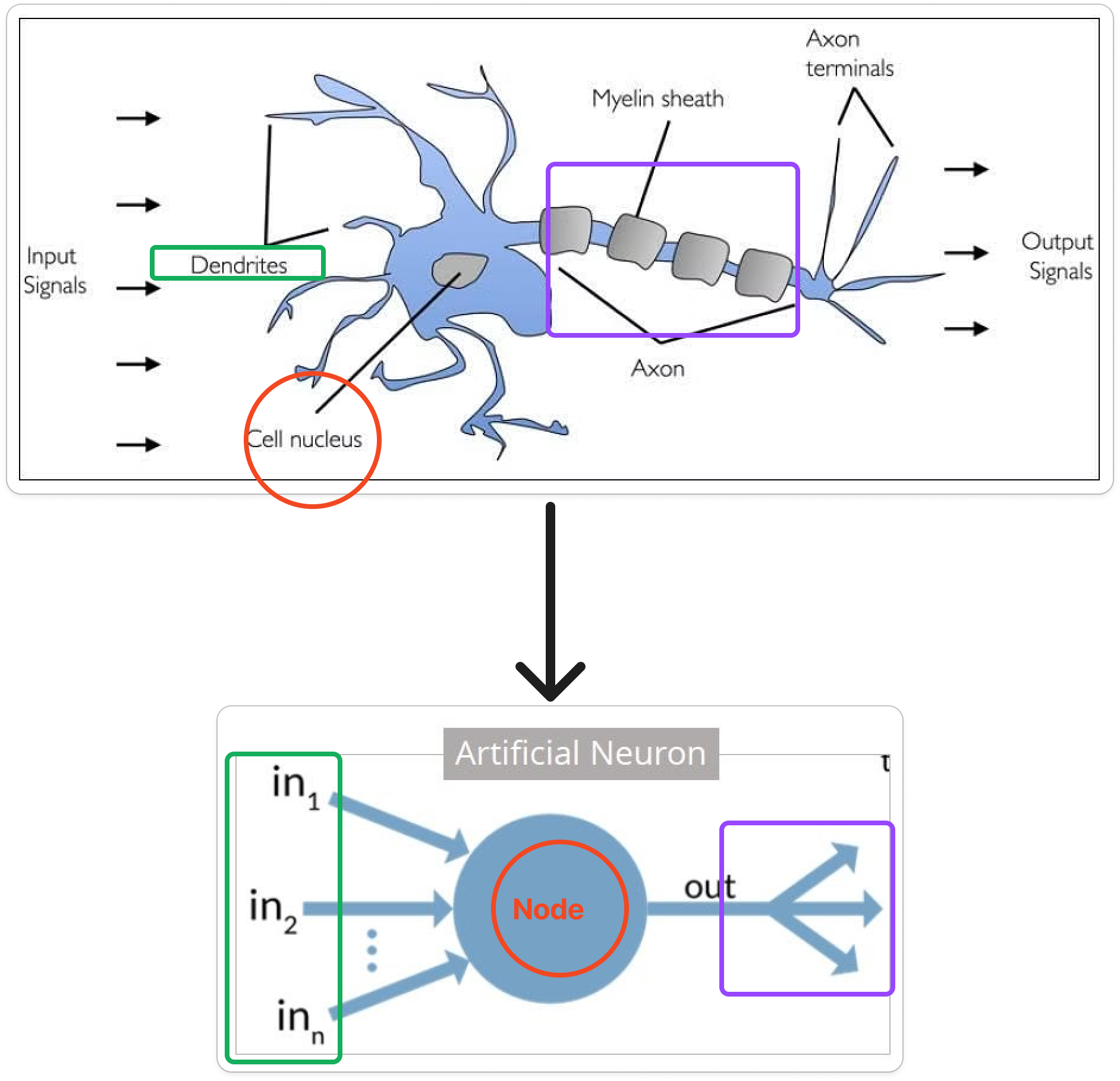
A human brain has billions of neurons. Neurons are interconnected nerve cells in the human brain that are involved in processing and transmitting chemical and electrical signals. Dendrites are branches that receive information from other neurons.
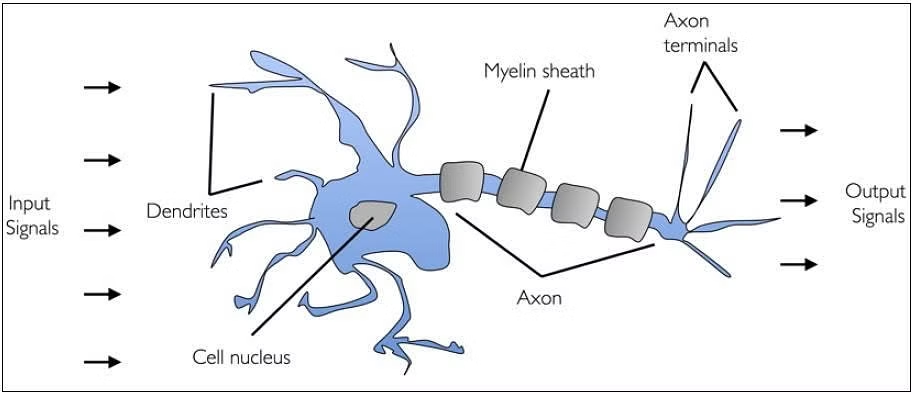
Cell nucleus or Soma processes the information received from dendrites. Axon is a cable that is used by neurons to send information. Synapse is the connection between an axon and other neuron dendrites.
Let us discuss the rise of artificial neurons in the next section.
Rise of Artificial Neurons
Researchers Warren McCullock and Walter Pitts published their first concept of simplified brain cell in 1943. This was called McCullock-Pitts (MCP) neuron. They described such a nerve cell as a simple logic gate with binary outputs.
Multiple signals arrive at the dendrites and are then integrated into the cell body, and, if the accumulated signal exceeds a certain threshold, an output signal is generated that will be passed on by the axon. In the next section, let us talk about the artificial neuron.
Artificial Neuron
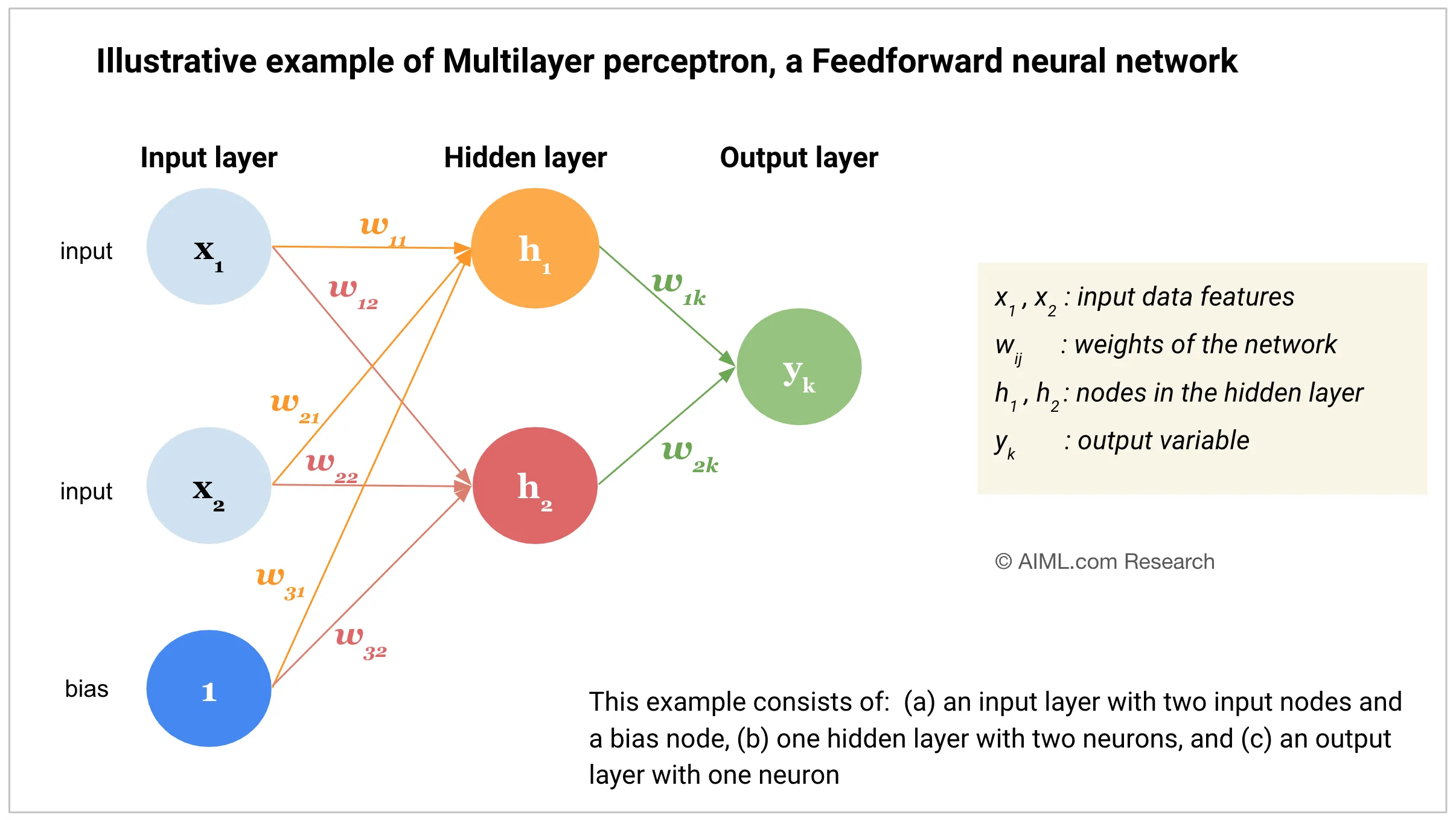
An artificial neuron is a mathematical function based on a model of biological neurons, where each neuron takes inputs, weighs them separately, sums them up and passes this sum through a nonlinear function to produce output.
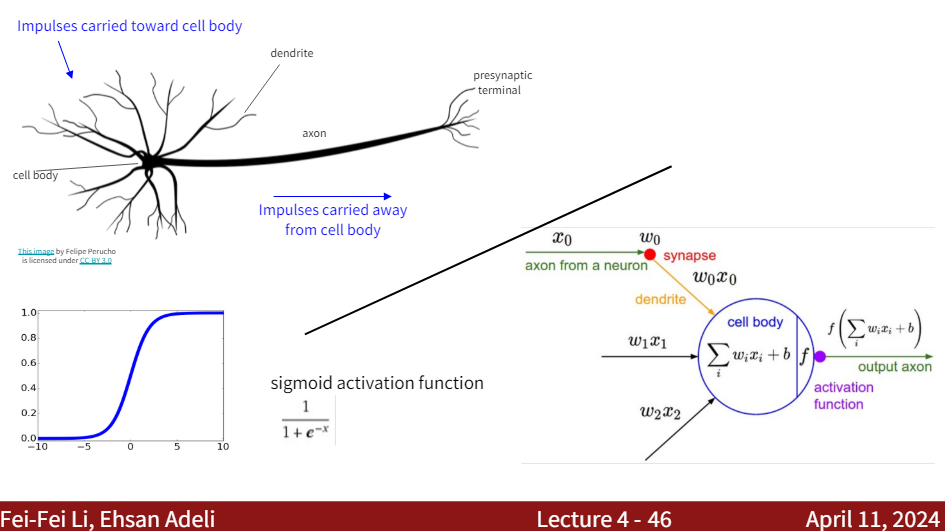
Slide reference: CS231n-lecture4-2024
Note: The artificial neuron is a simplified model of the biological neuron. Biological neurons are much more complex and have many more components than artificial neurons.
Biological Neurons:
- Many different types
- Dendrites can perform complex non-linear computations
- Synapses are not a single weight but a complex non-linear dynamical system
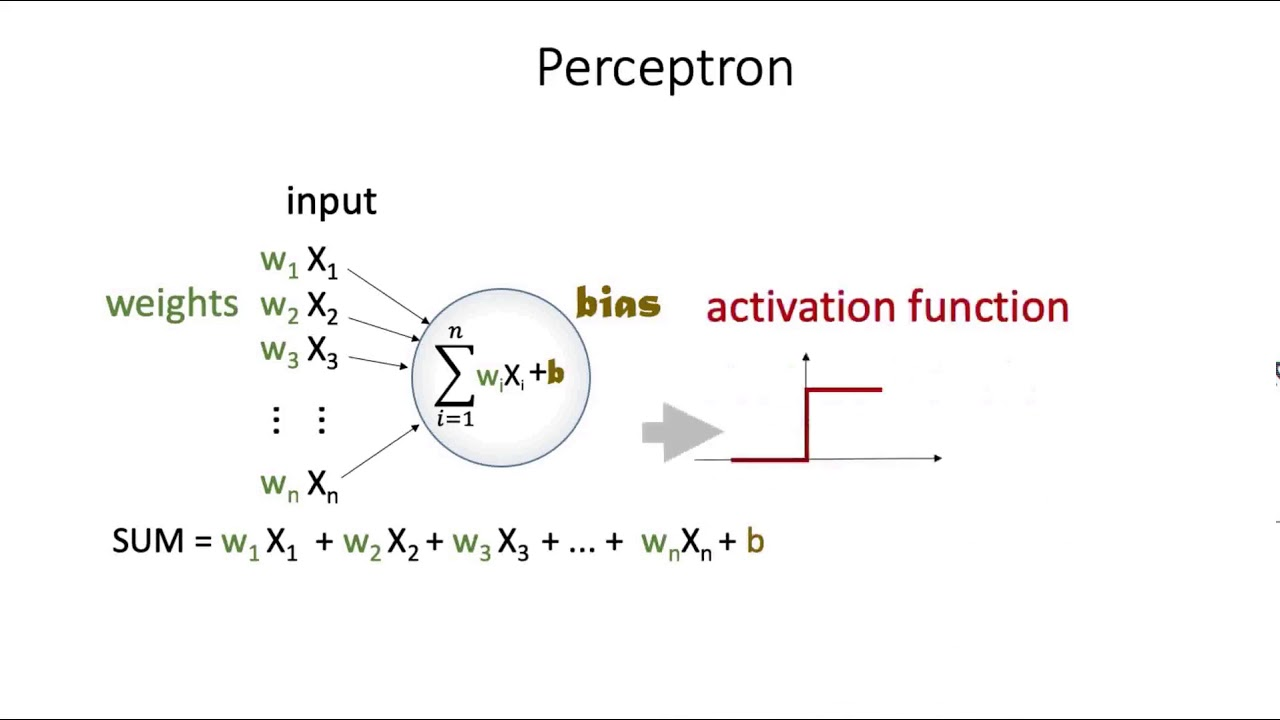
Perceptron
Perceptron was introduced by Frank Rosenblatt in 1957. He proposed a Perceptron learning rule based on the original MCP neuron. A Perceptron is an algorithm for supervised learning of binary classifiers. This algorithm enables neurons to learn and processes elements in the training set one at a time.
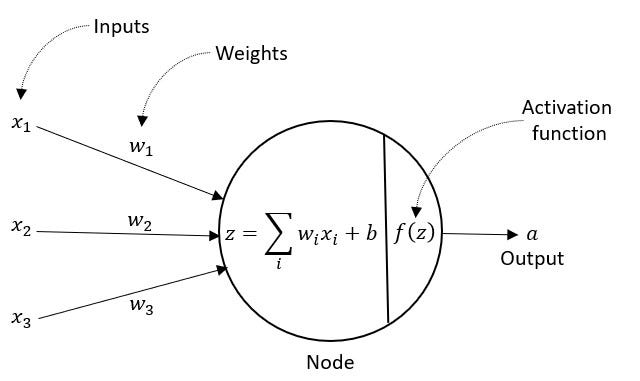
Components of Perceptron
A Perceptron consists of four main components:
- Input values or One input layer: The input layer receives the input values.
- Weights and Bias: Each input value is multiplied by a weight and then summed up. A bias is added to the sum.
- Net sum: The sum of the weighted input values and bias is calculated.
- Activation function: The net sum is passed through an activation function to produce the output. Common activation functions used in perceptron include the step function, sigmoid function, softmax function, and ReLU function.
- Output: The output of the perceptron is a single binary value, either 0 or 1, which indicates the class or category to which the input data belongs.
Types of Perceptron
Single-layer Perceptron
A single-layer perceptron is a feedforward neural network with a single layer of output units. It can only learn linearly separable patterns. The activation function used in a single-layer perceptron is the step function.
Multi-layer Perceptron
A multi-layer perceptron is a feedforward neural network with one or more hidden layers between the input and output layers. It can learn non-linear patterns. “Multi-layer” often refers to the neural network having more than one hidden layer. The activation function used in a multi-layer perceptron is usually the sigmoid function or the ReLU function.